
Introduction
The Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) data analysis project utilizes datasets from the Mapping Medicare Disparities by Population tool, a comprehensive resource designed to examine variations in healthcare access, utilization, and outcomes among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States.
This project utilized advanced data collection and analysis methods to investigate healthcare disparities using datasets from the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) spanning the years 2012 to 2016. Automated data downloads were performed using a Python Selenium script to streamline the collection process and ensure efficient access to data. The datasets provided detailed insights into demographic, geographic, and clinical factors that influence disparities in healthcare access, utilization, and outcomes.
Dynamic year-based weighting was populated to a Access database, this enabled accurate comparisons of population weights across different racial groups over multiple years. The visualizations developed during the project offered a comprehensive understanding of how healthcare disparities vary across age groups, racial demographics, and geographic locations.
Objective
To analyze disparities in Medicare healthcare access, utilization, and outcomes across populations of all age groups, particularly focusing on those below 65 and older, based on demographic factors such as race, ethnicity, and gender. This study leverages the Mapping Medicare Disparities by Population dataset to identify trends in healthcare services, health outcomes, and associated inequities.
By employing advanced data analysis techniques, including year-specific weighting through an Access database, this project provides researchers and policymakers with data-driven insights into the healthcare needs and challenges faced by the aging population. The findings aim to:
- Inform evidence-based strategies for improving healthcare equity and efficiency.
- Encourage proactive interventions to address disparities among vulnerable groups.
- Support public awareness of healthcare trends, empowering communities to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Methodology
- Data Collection: Worked on a Python Selenium script to automate the download of data from the CMS website and populated to a Microsoft Access database with year-specific population weights.
- Data Preparation: Cleaned, standardized, and merged datasets to create a unified database for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Identified disparities by race, ethnicity, and geography using statistical methods and year-based weighting to track trends over time.
- Populate the data: Populate the collected data to the table in access database
- Visualizations and Reporting: Generated actionable insights, visualizations, and evidence-based recommendations to address healthcare disparities and improve equity.
Work Flow

Results
Trends over time by age group
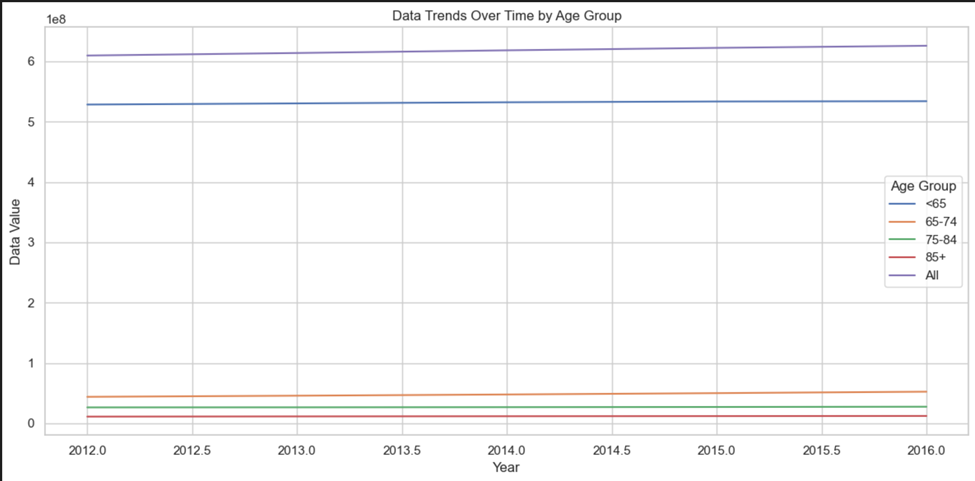
- Data trends across all age groups remain stable from 2012 to 2016, with no significant changes.
- The “All” category consistently shows the highest values as it aggregates all age groups.
- The “<65” age group has higher values compared to other individual age groups.
- The “65-74,” “75-84,” and “85+” age groups exhibit similar, lower values.
- The stability suggests uniformity in healthcare metrics over time for all age groups.
Demographic distribution of data values by race and age group
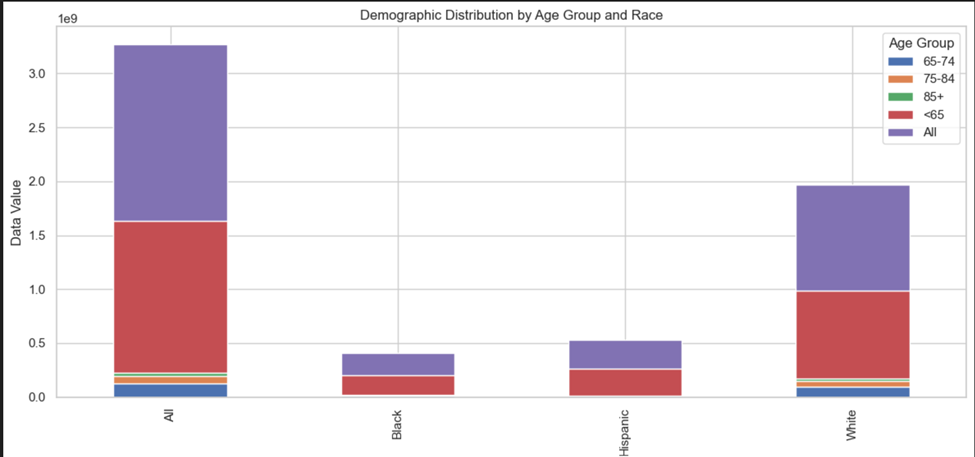
- The “All” category has the highest overall data value, combining all age groups and races.
- Among racial groups, the “White” demographic exhibits the largest data values, significantly surpassing “Black” and “Hispanic.”
- The “Black” and “Hispanic” demographics have similar patterns, but their values are notably lower compared to “White.”
- The “85+” and “<65” age groups contribute significantly across all racial categories, with visible proportions in stacked segments.
- Smaller age groups like “65-74” and “75-84” have relatively minimal contributions, visible as thin segments in the bar chart.
- This distribution highlights racial disparities, with “White” dominating across all age groups and overall metrics.
Geographic distribution of data values across years
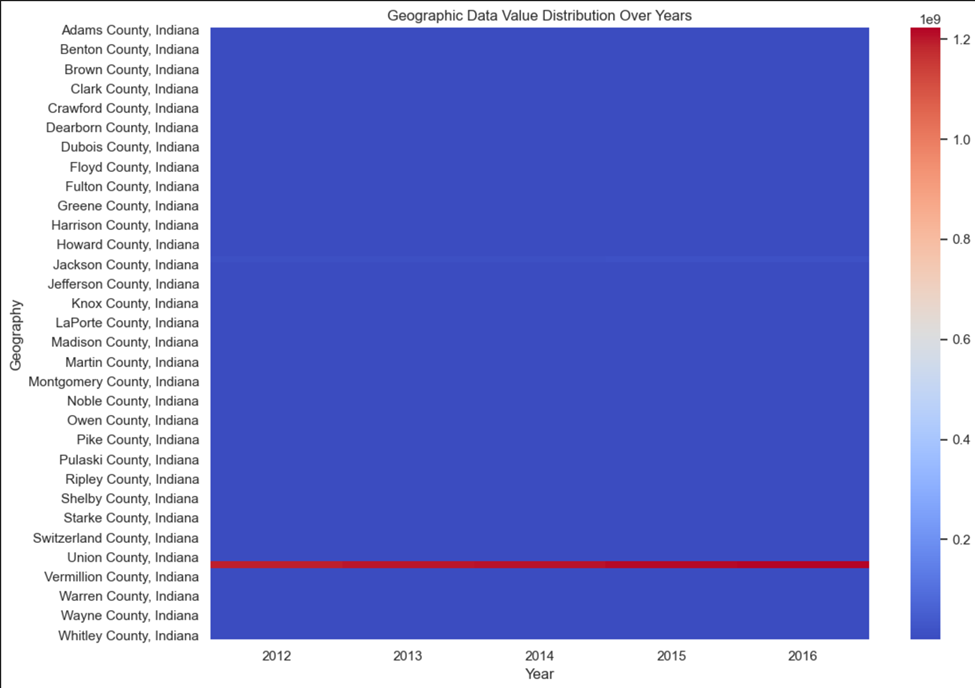
- Most counties in Indiana exhibit low data values, as indicated by the dominant blue color in the heatmap.
- A few counties, such as Vermillion County, show significantly higher data values, represented by the red regions.
- Data values remain consistent over the years (2012–2016) for most counties, with no noticeable yearly variations.
- The distribution highlights stark geographic disparities, where only a small number of counties have high data values.
- The concentration of high values in specific counties could indicate localized factors influencing the data metrics.
Distribution of data values by age group
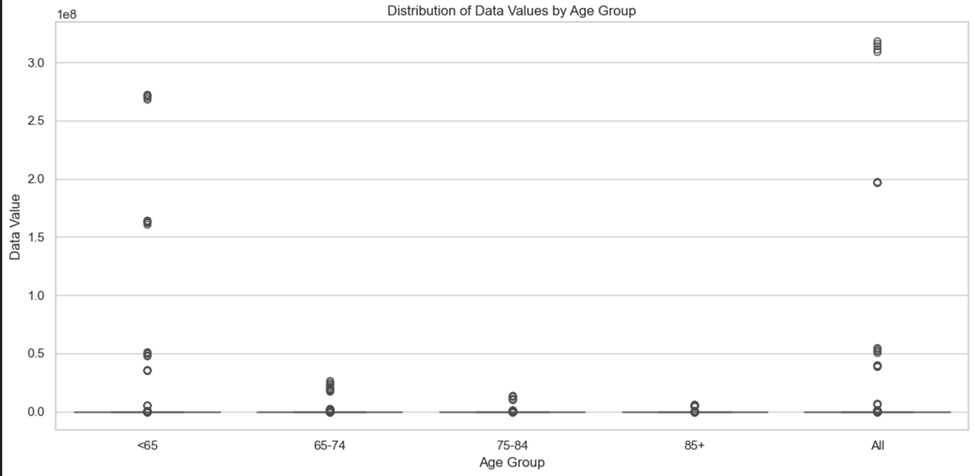
- The “All” category has the widest range of data values, with the highest outliers, indicating it includes aggregated data across all age groups.
- The “<65” age group shows a few high outliers, suggesting significant variations in specific data points within this group.
- Age groups “65-74,” “75-84,” and “85+” exhibit similar distributions with smaller ranges and fewer outliers.
- Most data points are concentrated near lower values for all age groups, indicating skewed distributions.
- The presence of outliers in multiple age groups suggests disparities or unusual cases that may require further investigation.
Summary
This project focused on analyzing disparities in healthcare access, utilization, and outcomes using data from the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS). The study integrated datasets from the Mapping Medicare Disparities by Population tool, automating data collection with Python Selenium scripts to ensure the inclusion of up-to 2022 data. Dynamic year-based weighting was applied using an Access database to enhance the accuracy and representativeness of the analysis.
Key methodologies included weighted mean calculations, data segmentation by age, race, and geography, and the creation of visualizations to highlight trends and disparities. Insights revealed significant differences in healthcare metrics across demographics, particularly among racial and age groups. These findings underscore systemic disparities, with some populations consistently showing higher or lower utilization rates and outcomes.
The visualizations provided actionable insights into demographic and geographic disparities, supporting targeted policy-making and resource allocation. By highlighting trends in healthcare utilization and outcomes for Medicare beneficiaries, this project offers valuable information for researchers, policymakers, and healthcare experts to address inequities and improve care delivery. Additionally, it empowers communities with knowledge about healthcare trends, encouraging informed decision-making and proactive interventions.
Team Members
| Name | Role |
|---|---|
| Hasaranga Jayathilake | Lead Data Analyst |
| Supraja Pericherla | Lead Data Analyst and Project Manager |
| Mani Teja Ladi | Data Analyst |
| Shreya Reddy Kunchala | Data Analyst |
| Varsha Reddy Madireddy | Data Analyst |
| Amirta Varshini Natarajan | UI/UX Designer |
| Narasimha Rohit Katta | Web Developer |